Mastering Automotive Mechanics and Electronics: A Comprehensive Guide
The world of Automotive Mechanics And Electronics is constantly evolving, demanding a deeper understanding of both traditional mechanical systems and cutting-edge electronic technologies. Today’s vehicles are intricate machines, relying heavily on the seamless integration of mechanics and electronics to deliver performance, safety, and comfort. This article delves into the core aspects of this fascinating field, exploring its complexities and how advancements are shaping the future of driving.
Modern vehicles are a symphony of mechanical and electronic components working in perfect harmony. From the engine’s intricate combustion process to the complex network of sensors and control units, a solid grasp of both disciplines is crucial for any automotive professional. The role of an ase certified master automotive technician requires extensive knowledge, not just about nuts and bolts, but also about diagnostic software, electronic control modules, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). This fusion of mechanics and electronics isn’t just a trend; it’s the bedrock of contemporary automotive engineering.
The Interplay of Mechanical and Electronic Systems
The foundation of automotive mechanics lies in understanding fundamental principles like thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, and materials science. This knowledge is essential for comprehending how engines, transmissions, suspensions, and braking systems function. However, these mechanical systems are increasingly controlled and monitored by electronic components. Consider the modern engine; fuel injection, ignition timing, and variable valve timing are all electronically managed to optimize performance and emissions. Similarly, advanced braking systems such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and electronic stability control (ESC) rely on electronic sensors and control units to enhance vehicle safety. Understanding how these systems interact is paramount.
Why Integration Matters
The integration of mechanical and electronic systems isn’t merely about adding complexity, it’s about improving performance, efficiency, and safety. For instance, electronic power steering (EPS) replaces traditional hydraulic systems with an electric motor, providing a more precise steering feel and reducing fuel consumption. Likewise, the advent of hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs) has blurred the lines between mechanical and electronic engineering, creating a need for technicians who are adept at both disciplines.
“The future of automotive repair is undeniably intertwined with electronics,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a lead automotive engineer. “A mechanic needs to be fluent in both traditional mechanical skills and the intricacies of computer-controlled systems to diagnose and repair vehicles effectively.”

This fusion has created new challenges and opportunities for individuals seeking careers in the automotive sector. From traditional mechanics needing to learn about electronic diagnostics to software engineers delving into embedded systems, the automotive industry is a playground for diverse talent.
Key Areas of Automotive Mechanics
Automotive mechanics encompasses numerous sub-disciplines. Here are some key areas:
- Engine Repair and Maintenance: This involves a deep understanding of the internal combustion engine, its components, and the processes that allow it to convert fuel into motion. It includes everything from replacing spark plugs to rebuilding complete engines.
- Transmission and Drivetrain: This area focuses on the components that transmit power from the engine to the wheels, including manual and automatic transmissions, differentials, and driveshafts.
- Suspension and Steering: Suspension systems are responsible for vehicle stability, handling, and ride comfort. This area also covers steering systems and wheel alignment.
- Braking Systems: This area involves maintaining and repairing various braking components, including brake pads, rotors, calipers, and hydraulic lines.
- Exhaust Systems: The exhaust system handles the removal of waste gases from the engine and includes components like catalytic converters and mufflers.
Core Elements of Automotive Electronics
The electronic side of things is equally vast and complex. Here are some key elements:
- Sensors and Actuators: These devices monitor and control different aspects of vehicle operation, from engine temperature to wheel speed, using electronic control units (ECUs).
- Electronic Control Units (ECUs): These are the brains of the operation, using software to interpret data from sensors and control actuators. They manage everything from fuel injection to transmission shifting.
- Networking and Communication: Vehicles use a variety of communication protocols like CAN (Controller Area Network) to allow different systems to communicate and share information.
- Infotainment and ADAS: Modern vehicles feature sophisticated infotainment systems, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) including adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist, and increasingly, autonomous driving capabilities.
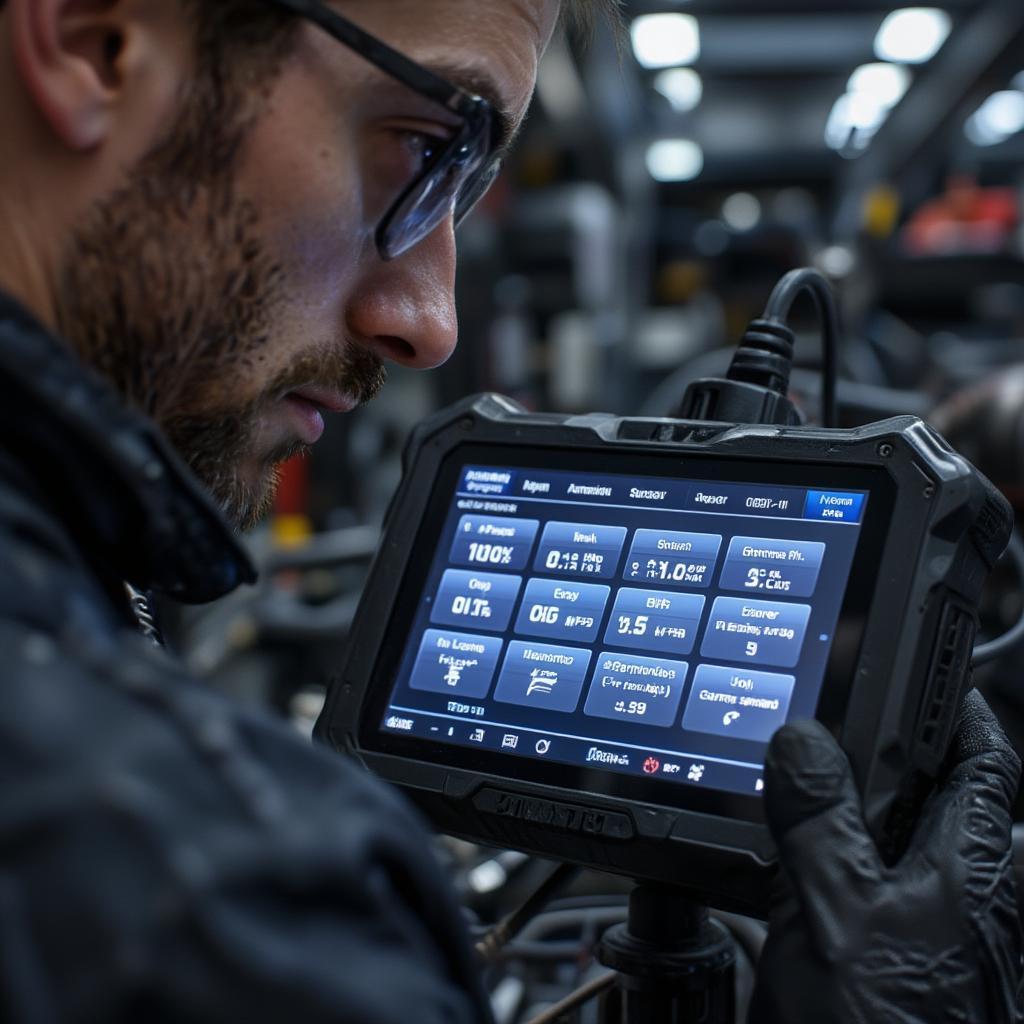
- Diagnostics and Troubleshooting: Electronic diagnostics relies on specialized tools and knowledge to identify and repair issues with the vehicle’s complex electrical and electronic systems.
Understanding the interplay between these areas is critical for efficient troubleshooting and maintenance. For those seeking comprehensive knowledge, resources like automotive technology a systems approach 7th edition pdf can prove invaluable.
The Impact of Technology on Automotive Systems
The automotive industry has been significantly impacted by technological advancements over the years. Here’s how technology is reshaping both the mechanics and electronics of vehicles:
Enhanced Diagnostics
Modern diagnostic tools have revolutionized the way vehicles are repaired. Scan tools and other diagnostic equipment allow mechanics to quickly identify problems by reading error codes stored in the ECUs. This reduces downtime and increases efficiency.
Electrification
The rise of hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs) has introduced new challenges and opportunities. These vehicles have complex electric powertrains, high-voltage battery systems, and advanced electronic controls, requiring mechanics to have a deep understanding of both mechanical and electrical systems. Furthermore, the introduction of new technologies, such as regenerative braking and battery management systems, calls for specialized knowledge.
Autonomous Driving
The development of autonomous vehicles is one of the most significant technological leaps in the automotive industry. These vehicles rely on a complex network of sensors, cameras, radar, and lidar, along with sophisticated AI algorithms, to navigate roads and make real-time driving decisions. As such, expertise in both automotive electronics and software development is becoming increasingly crucial.
“The speed of technological advancement in the automotive industry is astounding,” says Michael Thompson, a senior automotive technician. “Staying updated on the latest electronic systems and repair techniques is critical for mechanics to remain competitive.”
Training and Education in Automotive Mechanics and Electronics
Pursuing a career in automotive mechanics and electronics requires rigorous training and education. There are multiple pathways that one can take to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills. Some of those are:
Vocational Training Programs
These programs offer hands-on training in automotive repair, maintenance, and diagnostics. Students learn about various mechanical systems as well as the use of diagnostic tools. These programs are ideal for those seeking immediate entry into the workforce, with options like automotive repair training that help individuals acquire the necessary certifications and experience to excel in the field.
Associate’s and Bachelor’s Degrees
For those interested in engineering roles or management positions, pursuing a degree in automotive technology or related fields is beneficial. These programs often combine theoretical knowledge with practical hands-on experience, providing a strong foundation for advanced roles in the automotive sector. There are also various universities with automotive programs that offer specialized programs in this field.
Online Courses and Certifications
Various online courses and certification programs can supplement formal education, and enhance knowledge and skills in specific areas. These courses provide convenient and flexible learning options, ideal for those already working or individuals seeking to expand their expertise in specific areas.
Importance of Foundational Knowledge
Regardless of the path chosen, having a strong foundation in basic automotive mechanics and electronics is essential. Concepts like thermodynamics, circuit theory, and digital electronics are indispensable, particularly when transitioning to more complex topics. basic mechanic classes can be beneficial for starting your journey.
Staying Updated with Advancements
Given the pace of technological advancement in this field, continuing education is essential. Mechanics must stay abreast of new technologies and techniques to effectively repair and maintain modern vehicles.
The Future of Automotive Technology
The field of automotive mechanics and electronics is set to undergo rapid evolution in the coming years. Emerging trends such as:
- Increased Electrification: Electric vehicles will become more dominant, requiring mechanics with expertise in battery management, electric motor repair, and high-voltage systems.
- Autonomous Driving: Autonomous vehicle technology will demand skilled technicians capable of maintaining complex sensor arrays, sophisticated software systems, and advanced control units.
- Connectivity: Vehicles will become increasingly connected, relying on intricate networks to communicate with other vehicles, infrastructure, and the cloud.
- Advanced Materials: New materials will be used in vehicle construction, requiring mechanics to adapt their repair techniques.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI will play a bigger role in diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and vehicle performance optimization.
These trends highlight the need for well-rounded professionals who have expertise in both mechanical and electronic systems. The integration of these two areas will only become stronger, creating exciting challenges and opportunities in the automotive industry.

Conclusion
Mastering automotive mechanics and electronics requires a blend of practical skills, technical expertise, and a passion for continuous learning. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, professionals who are adept at both disciplines will be highly sought after. Whether you are a seasoned mechanic looking to expand your knowledge or an aspiring technician embarking on a new career path, the future of automotive mechanics and electronics is brimming with potential. By embracing both the mechanical and electrical aspects of vehicle operation, you can pave the way for a successful career in this dynamic and constantly evolving field of automotive mechanics and electronics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the key differences between automotive mechanics and automotive electronics?
Automotive mechanics focuses on the physical components of a vehicle such as engines, transmissions, and suspensions, while automotive electronics deals with the electrical and electronic systems including sensors, ECUs, and infotainment systems.
2. How is technology impacting the field of automotive mechanics?
Technology has transformed the field by introducing electronic diagnostic tools, hybrid and electric vehicles, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), requiring mechanics to have a broader skill set that includes electronics.
3. What education and training is needed to become an automotive mechanic?
Vocational training programs and associate’s degrees offer hands-on training while bachelor’s degrees are suitable for advanced roles. It’s also helpful to seek certifications and continue learning to stay updated on technological advancements.
4. What are the challenges of working with automotive electronics?
Working with automotive electronics requires a strong understanding of circuit theory, digital electronics, and diagnostic tools. It also requires staying abreast of new technologies, which can change rapidly.
5. Is it possible to specialize in either mechanics or electronics within the automotive industry?
Yes, while a solid understanding of both is beneficial, it is possible to specialize in either field, focusing on specific systems or vehicle types. Specialization allows for deep expertise in a particular area.
6. What are some of the emerging trends in automotive mechanics and electronics?
Emerging trends include increased electrification, autonomous driving technology, vehicle connectivity, use of advanced materials, and the growing use of artificial intelligence. These trends will reshape the industry in significant ways.
7. How has the integration of mechanics and electronics affected car repair?
The integration has led to more complex repair procedures and diagnostics. Mechanics now need to understand both mechanical systems and electronic control units to perform effective repairs.
8. What skills are essential for a modern automotive technician?
A modern technician requires expertise in both mechanical and electronic systems, good problem-solving abilities, proficiency with diagnostic tools, and the ability to adapt to new technologies.
9. What is the significance of ECUs in modern vehicles?
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) act as the brains of the vehicle, controlling a range of systems, from fuel injection to transmission shifting, making them a crucial aspect of modern automotive technology.




