Dog Reproductive Anatomy Female: Understanding Structure and Function for Better Care
Dog reproductive anatomy female is a captivating study of intricate systems that not only ensure the survival of the species but also shape the relationship between humans and their canine companions. The female dog’s reproductive system, often affectionately referred to with terms like “bitch,” is an elegant structure designed for both mating and nurturing life. This article delves into the remarkable features of this anatomy, its hormonal influences, and the broader implications of understanding these dynamics in our interactions with dogs.
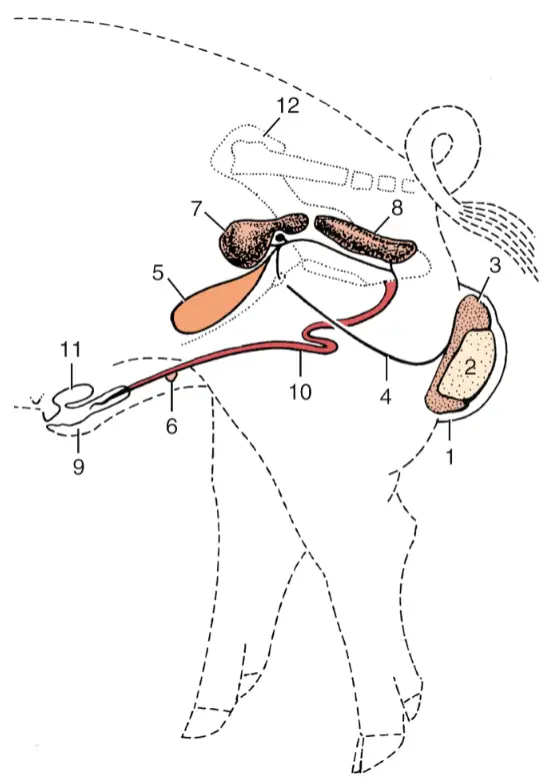
The Structure of the Canine Reproductive System

Understanding the female dog’s reproductive anatomy begins with an appreciation of its complexity and purpose. Each component of this system plays a vital role in ensuring effective reproduction and the nurturing of offspring.
Dog Reproductive Anatomy Female – The Vulva: An External Indicator

The vulva serves as the gateway to the female dog’s reproductive tract. It is more than just a physical structure; it reflects the internal physiological changes experienced during various stages of the estrous cycle.
During the proestrus phase, the vulva undergoes noticeable changes. It becomes swollen, accompanied by a discharge that signals readiness for mating. This transformation is not merely cosmetic; it serves as an essential communication tool among canines. Other dogs can detect these changes through scent, which plays a crucial role in attracting potential mates.
When observing a female dog in heat, one might liken this behavior to a performance—her body is sending signals that she is ready for the next chapter of her biological narrative. This external display fosters not only reproduction but also social bonding, further illustrating the interconnectedness of the canine community.
The Vagina: A Passageway to Fertility
Transitioning from the vulva, the vagina acts as a passage connecting the outer world to the inner workings of the reproductive system. Structurally engineered to accommodate various functions, the vagina serves as the entry point for sperm during mating.
Within the vagina, different layers of tissue provide elasticity and strength, enabling it to adjust to the demands placed upon it during copulation and subsequent birthing processes. The vaginal walls are lined with specialized cells that secrete fluids to create an optimal environment for sperm survival, reflecting nature’s foresight in ensuring reproductive success.
Moreover, understanding the vagina’s role emphasizes the importance of hygiene and care in female dogs. Regular veterinary check-ups can help monitor any unusual changes or issues within this vital organ, ultimately contributing to a dog’s overall well-being.
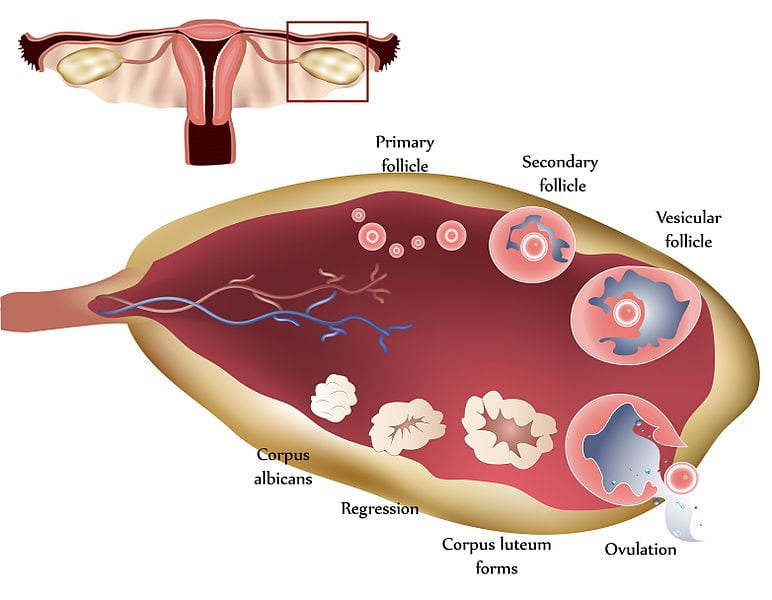
The Uterus: A Sanctuary for Embryonic Development

At the heart of the female dog’s reproductive anatomy lies the uterus—a nurturing sanctuary where fertilized eggs can develop into puppies. The uterus consists of two horns, each capable of supporting the growth of multiple embryos, showcasing an evolutionary advantage that allows for larger litter sizes.
The uterine lining, known as the endometrium, thickens in preparation for potential pregnancy. If fertilization occurs, this lining provides the necessary nutrients and protections for the developing embryos. In contrast, if no pregnancy takes place, the endometrial lining is shed, marking the transition back to the estrous cycle.
This cyclical nature of the uterus’s function represents an incredible adaptability in response to environmental conditions and breeding practices. From the perspective of a pet owner, understanding the nuances of uterine health can lead to better reproductive decisions, whether it involves spaying, breeding, or managing a dog during her heat cycle.
Hormonal Influences on the Female Cycle

The fascinating interplay of hormones shapes every aspect of a female dog’s reproductive cycle. These hormonal changes govern physical and behavioral alterations, defining the periods of receptivity and maternal instincts.
Estrous Cycle Phases: A Harmonious Dance

The female dog’s reproductive cycle comprises several phases: proestrus, estrus, diestrus, and anestrus. Each stage introduces unique hormonal shifts that dictate the female’s behavior and physiological state.
During proestrus, rising estrogen levels initiate the swelling of the vulva and the production of pheromones. This creates an inviting atmosphere for male dogs while simultaneously establishing boundaries against unwanted advances. As the female transitions into estrus, her receptivity peaks. Elevated progesterone levels coordinate the timing of ovulation, creating an urgent call for mating.
Interestingly, this cyclical rhythm can be likened to a meticulously choreographed dance. The ebb and flow of hormones are akin to music guiding each step, influencing acceptance of mates and fostering instinctual behaviors. Observing this cycle offers insights into the intricate balance between biology and instinct, revealing the profound connections between animals and their environments.
Maternal Instincts: Programming Through Hormones
Once fertilization takes place, the focus of hormonal influence shifts dramatically. Progesterone reigns supreme, preparing the female’s body for nurturing developing puppies.
This surge in hormones activates maternal instincts, shaping behaviors that facilitate the caring and protection of her young. Nesting behaviors often manifest as the mother prepares a safe space for her forthcoming litter. These instinctual actions highlight how deeply intertwined hormonal responses are with social structures and survival strategies.
Understanding these changes can significantly enhance the relationship between humans and dogs. Pet owners who recognize the signs of impending motherhood can offer appropriate support, ensuring that the female dog feels secure during this transformative phase.
Behavioral Changes: Navigating the Heat Cycle
The impact of hormonal fluctuations extends beyond physical changes; they also induce notable behavioral shifts. As a female dog transitions through her heat cycle, increased energy levels and assertiveness may become apparent.
During estrus, heightened libido can manifest in various ways. Some females may exhibit affectionate behaviors towards their human companions, while others may become more independent and curious about their surroundings. Recognizing these behavioral patterns empowers pet owners to respond appropriately, catering to the unique personality and needs of their dogs during this time.
Additionally, being cognizant of these behavioral changes can help mitigate potential conflicts with male dogs, ensuring that both canines and their humans navigate this period smoothly and safely.
Implications for Breeders and Pet Owners
An understanding of the female dog’s reproductive anatomy and hormonal cycles has far-reaching implications for breeders and pet owners alike. Responsible management of these cycles can significantly affect the health and well-being of both the mother and her offspring.
Optimal Breeding Practices: Timing and Techniques
For breeders, accurately charting the female dog’s reproductive cycle is paramount. Recognizing the optimal breeding window can maximize the chances of successful mating and healthy litters.
Utilizing tools such as hormone testing and monitoring physical signs can guide breeders in pinpointing the most advantageous times for breeding. Beyond mere technicalities, this practice embodies respect for the natural processes at play, emphasizing a holistic approach to breeding that values the health of the dog above all else.
Moreover, responsible breeders should prioritize genetic health by selecting pairs that complement each other’s strengths and weaknesses. This deeper understanding of reproductive anatomy paves the way for conscientious breeding practices that uphold the breed’s integrity and contribute positively to the canine population as a whole.
Behavioral Adjustment: The Role of Awareness
Pet owners benefit immensely from understanding the intricacies of the female dog’s reproductive cycle. Being aware of the changes associated with heat cycles enables owners to anticipate and manage behavioral adjustments, ensuring both the dog’s comfort and the household’s harmony.
For example, knowing when a female dog is in estrus can prevent accidental matings and unnecessary stress for both the dog and the owner. Creating a supportive environment for a dog experiencing her heat cycle ensures she remains calm and comfortable, allowing her to navigate this natural process with ease.
Furthermore, educating oneself on the importance of spaying or neutering can lead to informed decisions regarding reproductive health. By reducing the number of uncontrolled litters, responsible ownership contributes to the overall well-being of the canine population while promoting healthier and happier lives for individual dogs.
Enhancing Human-Canine Bonds
Ultimately, a deeper understanding of the female dog’s reproductive anatomy and cycles enhances the bond between humans and their furry companions. Knowledge breeds empathy, offering insights into the complexities of canine life that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Recognizing the significance of hormonal influences fosters a more profound appreciation for the unique experiences that female dogs undergo. This awareness opens the door to compassion-driven choices, whether it’s providing extra care during heat cycles or recognizing the need for a change in routine during pregnancy.
In learning about these dynamics, humans can embrace their roles as caregivers and advocates for their pets, deepening their relationships with their canine companions and enriching their lives together.
Conclusion

Understanding the female dog’s reproductive anatomy unveils a rich tapestry of biological complexity intertwined with instinctual behaviors. From the structural components that facilitate reproduction to the hormonal influences that guide cycles and behaviors, each element plays a critical role in the lifecycle of a female dog.
As we explore these intricacies, we gain valuable insights that extend beyond biology, informing our interactions with these cherished companions. Whether we are breeders striving for optimal outcomes or pet owners navigating the challenges of heat cycles, this knowledge fosters healthier relationships and more responsible decision-making.
Ultimately, appreciating the depth of the female dog’s reproductive anatomy enhances not only our understanding of canine life but also enriches our bonds with them, illuminating the pathway to a future where we can nurture, respect, and celebrate the beauty of the animal kingdom.