Understanding Weak Artificial Intelligence: Examples and Ethical Implications
Weak artificial intelligence, also known as narrow AI, is the type of artificial intelligence that is focused on performing a specific task, unlike the generalized human-like intelligence of strong AI. You’ve probably interacted with weak AI countless times today, perhaps without even realizing it. Let’s delve into what constitutes weak AI, explore some practical examples, and consider the ethical implications that arise from its widespread use.
What Exactly is Weak Artificial Intelligence?
At its core, weak AI is designed to excel at a defined function. These systems operate within pre-set parameters and lack the cognitive flexibility to adapt to scenarios they haven’t been explicitly programmed for. Unlike strong AI, which would theoretically mimic human consciousness and problem-solving abilities across a range of situations, weak AI cannot generalize its skills beyond its intended purpose. Think of it as a highly specialized tool rather than a versatile intellect.
Consider, for instance, a chess-playing AI. It may be capable of defeating even the world’s top grandmasters, but it is completely useless at tasks outside the realm of chess. It can’t drive a car, write a poem, or understand a joke. This narrow scope defines the essence of weak AI. In fact, many of the AI applications we interact with daily, from virtual assistants to recommendation systems, fall under this category. This reliance on specific functions is both a strength and a limitation.
Weak Artificial Intelligence Example in Everyday Life
To truly understand weak AI, let’s explore some tangible examples:
- Spam Filters: Email spam filters are a classic case of weak AI. These systems analyze incoming emails, identify patterns indicative of spam (such as specific keywords or suspicious links), and filter those messages into your spam folder. These filters learn from your interaction with email, but they cannot perform tasks beyond spam detection.
- Product Recommendation Systems: Online retailers use recommendation algorithms to suggest products you might like based on your previous purchases, browsing history, and similar user data. While highly effective at driving sales, these systems cannot engage in human-like conversation or offer genuine advice. They simply process data and follow pre-defined rules.
- Virtual Assistants: Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, while increasingly sophisticated, are still prime examples of weak AI. They can respond to your voice commands, set reminders, play music, and answer simple questions, but they operate within specific limitations. These tools do not have sentience and can only understand a narrow set of pre-programmed requests.
- Facial Recognition Systems: These systems are trained to identify faces and match them against databases. They are used for unlocking smartphones, tagging people in photos, and in security systems. However, their skills are limited to recognizing pre-trained facial structures and lack broader cognitive understanding.
- Game-Playing AI: AI systems designed to play specific games like chess, Go, or even complex video games demonstrate narrow AI. Though incredibly capable, their expertise is confined to the rules and parameters of the game they are designed for. These systems cannot apply their game-playing skills to other tasks.
These examples show that weak AI is already pervasive. They also highlight a critical aspect: each application is confined to its specific function.
Exploring the Subtleties: How Weak AI Functions
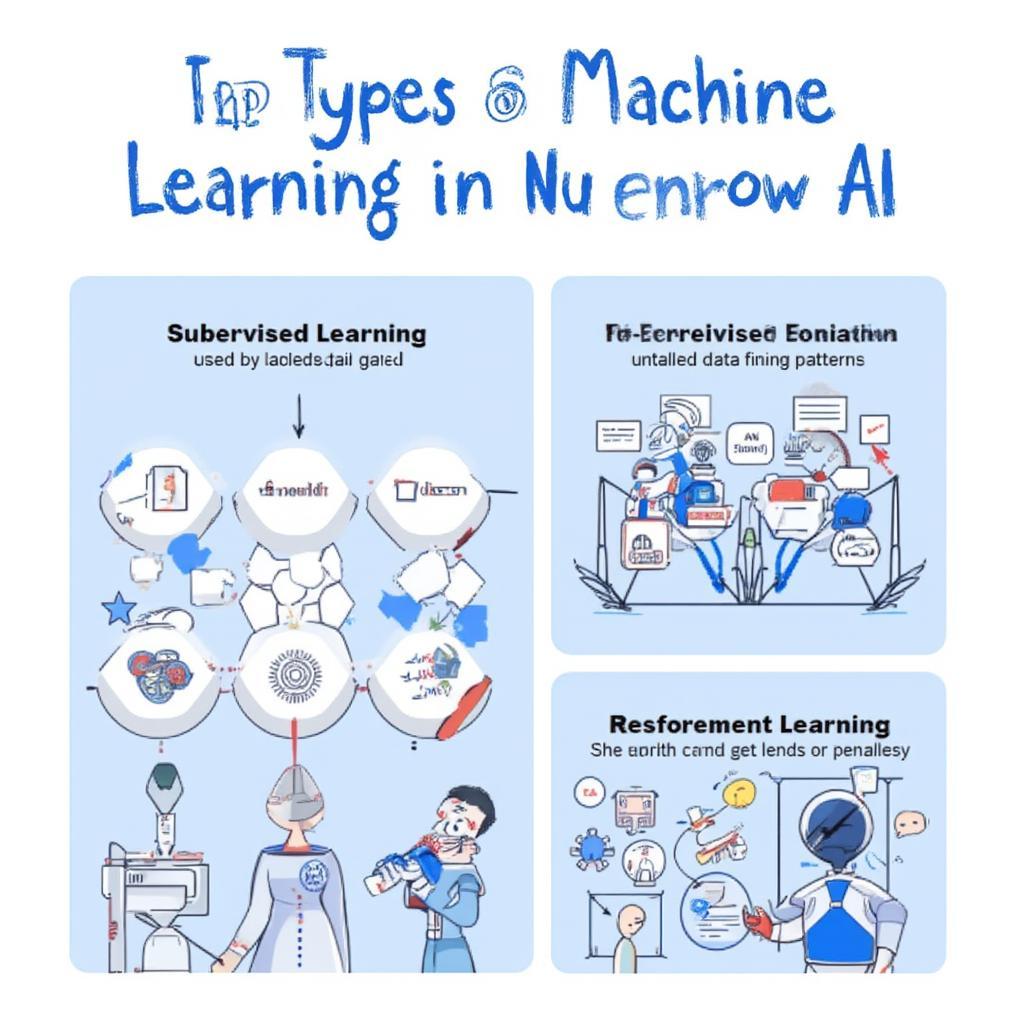
Weak AI functions through machine learning, often using techniques like supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Supervised Learning: The AI is trained on labeled data. For example, in spam filtering, the AI is provided with examples of both spam and non-spam emails, and it learns to classify emails based on these examples.
- Unsupervised Learning: The AI is trained on unlabeled data, and it tries to find patterns and relationships in the data. For instance, recommendation systems may use this to group users with similar preferences.
- Reinforcement Learning: The AI learns by interacting with an environment, receiving rewards for favorable actions and penalties for unfavorable ones. This approach is often used in game-playing AI.
The key here is that regardless of the approach, weak AI’s effectiveness stems from its specific training. This training sets the parameters within which the system operates.

Ethical Considerations: The Challenges of Weak AI
While weak AI has improved efficiency and convenience across a range of industries, it’s also important to acknowledge the ethical challenges that come with its growth.
- Bias: If the data used to train weak AI systems contains biases, these biases will be reflected in the system’s outputs. For example, a facial recognition system trained primarily on images of one ethnic group may be less accurate when used on other ethnic groups. This can cause real-world harm and perpetuate existing inequalities.
- Transparency and Explainability: Some weak AI systems, especially deep learning models, can be difficult to understand. This lack of transparency can make it challenging to identify and address potential issues. When an algorithm makes a critical decision, should we understand how it arrived at that decision?
- Job Displacement: As weak AI continues to automate tasks, there is a risk of job displacement in certain industries. This is not necessarily an AI problem, but a societal challenge that we have to navigate with the use of weak AI.
- Data Privacy: The development and use of weak AI systems often require the collection and use of large amounts of data. This raises concerns about data privacy and security. How should we be collecting data, how much data, and what happens when that data is breached or misused?
“The rapid advancement of weak AI has created remarkable opportunities, but it has also increased the need for ethical governance,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading AI ethicist. “We must prioritize fairness, transparency, and accountability in our systems to ensure that AI is a force for good.”
These ethical challenges need to be carefully considered as AI development continues to accelerate, otherwise, we risk creating systems that perpetuate bias and mistrust.
The Future of Weak AI: Current Trends and Potential Advancements
Despite its limitations, weak AI continues to evolve rapidly. Here are some current trends and potential advancements:
- Improved Accuracy and Efficiency: Machine learning algorithms continue to become more sophisticated, leading to improvements in accuracy and efficiency across all applications of weak AI. This means better spam filters, more accurate facial recognition, and more effective recommendations.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Weak AI is being increasingly integrated with other technologies such as the internet of things (IoT) and robotics. This leads to more automated and intelligent systems in homes, factories, and cities.
- Personalization: Weak AI will continue to enhance personalization experiences. From personalized news feeds to tailored education experiences, we can expect AI to make life more customized.
- Ethical Development: There is growing awareness of the ethical challenges of AI, which will lead to better policies and guidelines for the development of AI and its usage. This will result in fairer, more transparent, and accountable systems.
The next few years will be crucial for shaping the future of weak AI. We have the opportunity to create systems that not only enhance our lives, but also uphold our values.

Moving Forward: Why Ethical Considerations Matter
As we see the impact of weak AI on our daily lives, it is important to maintain a balanced perspective. While its capabilities are impressive, it is essential to remember that AI systems are created by humans. Because of this, we have a duty to ensure that they are created fairly and ethically.
Understanding that even weak AI has significant ethical implications helps us move forward with a sense of purpose. We need to create not just effective technologies, but just and inclusive ones. We must strive for more explainable and accountable systems. By doing this, we are ensuring that we are able to take full advantage of the great potential of weak AI while still protecting our human values.
“The ethical development of AI requires us to ask ourselves not just what can we do with this technology, but what should we do,” says Professor Kenji Tanaka, an expert in AI policy. “This is a crucial difference that we must keep in mind as we move forward.”
We must continuously educate ourselves about AI and engage in the discussion surrounding its ethical development. By having these discussions, we can ensure that as AI continues to evolve, it continues to benefit the whole of society. This includes making an effort to learn more about the basics of AI, such as artificial intelligence course engineering, to help build a better understanding of the underlying tech.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Weak AI
In conclusion, weak artificial intelligence, while narrow in scope, plays a crucial role in our daily lives. From simple spam filters to complex recommendation systems, these applications are continuously evolving. However, we cannot ignore the ethical considerations. By understanding [Weak Artificial Intelligence Example] and its implications, we can move towards building a more sustainable, responsible, and beneficial future with AI, where technology serves humanity and is not the other way around. Understanding the fundamentals, such as data science and artificial intelligence course, also helps in this process.